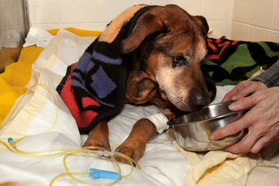
Defining “Quality of Life”
Courtesy of Moira Anderson Allen, M.Ed.
Copyright © 2001 by Moira Allen.
|
Whenever one considers the painful choice of euthanasia, one is always advised to take the pet’s “quality of life” into account. But what is “quality of life”? How can you determine whether a pet is still experiencing a good quality of life—or whether its level of suffering is no longer acceptable?
That decision is individual to every pet, and every owner. Following, however, are some factors to consider when attempting to assess a pet’s quality of life: |
Mobility.An older pet often loses mobility. A dog may no longer be able to climb stairs or hop into a car; a cat may lose the ability to jump onto a bed or chair. At this stage, however, your pet may still be healthy and happy, and you can easily make accommodations for its reduced ability.
If, however, your pet can barely move, that’s another matter. Can your pet get to its feet without assistance? Can it sit or lie down without collapsing? Can it walk? Can it handle basic functions, such as squatting on a litterbox? Does it whimper or growl if you attempt to move it?
I’ve seen dogs so crippled with hip dysplasia that they literally had to drag their immobilized hindquarters across the floor; this hardly represents the “quality of life” I want for my pets.
Appetite/Eating Ability. Is your pet able to eat? Can it consume enough food (or digest that food) to remain properly nourished? Does it regurgitate immediately after eating? Is it unable to chew, or does it have difficulty swallowing? Does it enjoy eating, or do you have to coax every bite past its lips? A pet that is unable to eat or gain sufficient nourishment from its food is on a slow road to starvation.
Breathing. A number of illnesses, including cancer, can affect the lungs. When a condition causes the lungs to fill with fluid or foreign matter (such as cancer cells), a pet quickly loses its ability to breathe easily or comfortably. You’ll notice that your pet may seem to be panting, or that it is laboring to breathe; often, you’ll see its stomach or flanks “pumping” as it can no longer breathe with just the chest muscles. It may also experience wheezing attacks. If such symptoms
occur, ask for a chest x-ray to determine the condition of the lungs. If the problem is due to an allergy, infection, or asthma, medication may help; if it is due to fluids that are the result of cancer or a heart condition, however, little can be done.
Discomfort. It can be difficult to determine whether a pet is in pain, as animals instinctively mask discomfort as much as possible. You can pick up clues, however, by watching its posture and expression. Does your pet’s face appear furrowed or “worried”, rather than relaxed and happy? Does it sit hunched or “hunkered” and tense, rather than relaxing and lying down? Lack of mobility can also be a sign of pain.
Another indication of pain is “denning.” An animal in pain will seek a safe place where it won’t be disturbed by other animals. If your pet has forsaken its usual territories or sleeping places for the back of the closet or a spot under the bed, this may be a sign that it is pain or distress and feels vulnerable.
A more obvious indication of pain is a pet’s reaction to touch. If your pet responds to touch by flinching away, hissing, snarling, or even snapping, this is a clear indication of pain. Sometimes this can indicate a localized pain; if the pet doesn’t want to be touched at all, however, it may indicate a broader discomfort.
Incontinence. Many pet owners feel terribly guilty over the natural annoyance they feel when a pet becomes incontinent. They feel they should be more loving, more patient. Incontinence, however, can also be stressful for the pet. As a basic survival mechanism, animals learn not to “mess where they sleep” (for the smell would draw attention to the location of one’s den). When an animal can no longer control when or where it urinates or defecates, you can be sure it is not happy with the situation.
Mental Capacity. Older pets occasionally develop signs of diminished mental capacity. They may seem to “forget” things, such as where a toy is located or what a command means. Such a pet may become confused by its surroundings, and this confusion can develop into fear. (In some cases, this “confusion” may be the result of hearing or vision loss, to which both you and your pet can often adapt.)
Happiness. Determining whether your pet is “enjoying” life is certainly a subjective decision. However, if you have been a keen observer of your pet’s behavior and attitude during its lifetime, you are likely to be able to determine when it no longer seems “happy.” You’ll know when it no longer seems to take any pleasure from its food, its toys, its surroundings—and most of all, from contact with you and the rest of its family. Most pets are tremendously easy to please; when it no longer becomes possibly to raise a purr or a tail-wag, you can be fairly certain that your pet is receiving little joy from life.
Response to Treatment. When a pet becomes ill, our natural response is to provide whatever treatment we can. This may mean tests, medications, even surgery. But drugs have side effects, repeated trips to the vet cause emotional distress, and more invasive treatments take a physical toll. Eventually, we may conclude that our efforts to treat a pet’s illness are more stressful to the pet than the condition itself—and that our efforts to save a pet’s life are actually diminishing, rather than enhancing, the quality of that life.
Making a Decision. Assessing a pet’s quality of life is an ongoing process, not a one-time decision. Initially, we’re likely to attempt to compensate for the problems we see. Pain medication may relieve a pet’s discomfort and improve its mobility. A change in diet may improve a pet’s appetite or provide better nutrition. We may resolve that we’re willing to clean up after a pet and carry it wherever it needs to go, for as long as necessary. But eventually such measures will cease to be effective. The process of assessing “quality of life” is really a question of determining (and deciding) when that point has been reached—and what you intend to do next.
It is often tempting, at this point, to postpone a decision still longer by deciding to “let nature take its course.” Before choosing that course of action (or inaction), however, it’s important to understand that, as a pet owner, you have been thwarting the “course of nature” from the beginning. By ensuring that your pet has food and shelter and is protected from predators, you have already guaranteed that nature will not take its course. By providing medical treatment, you have prolonged the life of your pet far beyond what it could have expected if left to “nature.” In nature, an animal that becomes too ill to obtain food or protect itself will perish quickly, though not necessarily comfortably.
Nor does nature necessarily offer an “easy” death even if you choose to let it “take its course” in the comfort of your home. An animal that cannot breathe easily, cannot eat or digest food properly, cannot control its bodily functions, and can scarcely move or enjoy human contact because of pain, is hardly dying “comfortably.”
This is really what the “quality of life” issue is all about. By usurping nature’s role throughout the life of our pets, we must sometimes also accept its role in determining (and bringing about) the death of a pet. To accept this, we may also have to accept that, in some cases, the quality of life we’re really trying to protect is our own: That we’re allowing our pet to suffer
out of a desire to avoid the anguish we know that we will experience when it dies. And that, ultimately, is the most unselfish act of love we can offer: To end a pet’s suffering, we must choose to accept our own.
Copyright © 2001 by Moira Allen. Reprinted from The Pet Loss Support Page - http://www.pet-loss.net. If you’re grieving the loss of a pet, you’ll find more helpful tips in Moira Allen’s book,
Coping with Sorrow on the Loss of Your Pet, available from Amazon.com at
http://www.amazon.com/exec/obidos/ASIN/1598584537/
If, however, your pet can barely move, that’s another matter. Can your pet get to its feet without assistance? Can it sit or lie down without collapsing? Can it walk? Can it handle basic functions, such as squatting on a litterbox? Does it whimper or growl if you attempt to move it?
I’ve seen dogs so crippled with hip dysplasia that they literally had to drag their immobilized hindquarters across the floor; this hardly represents the “quality of life” I want for my pets.
Appetite/Eating Ability. Is your pet able to eat? Can it consume enough food (or digest that food) to remain properly nourished? Does it regurgitate immediately after eating? Is it unable to chew, or does it have difficulty swallowing? Does it enjoy eating, or do you have to coax every bite past its lips? A pet that is unable to eat or gain sufficient nourishment from its food is on a slow road to starvation.
Breathing. A number of illnesses, including cancer, can affect the lungs. When a condition causes the lungs to fill with fluid or foreign matter (such as cancer cells), a pet quickly loses its ability to breathe easily or comfortably. You’ll notice that your pet may seem to be panting, or that it is laboring to breathe; often, you’ll see its stomach or flanks “pumping” as it can no longer breathe with just the chest muscles. It may also experience wheezing attacks. If such symptoms
occur, ask for a chest x-ray to determine the condition of the lungs. If the problem is due to an allergy, infection, or asthma, medication may help; if it is due to fluids that are the result of cancer or a heart condition, however, little can be done.
Discomfort. It can be difficult to determine whether a pet is in pain, as animals instinctively mask discomfort as much as possible. You can pick up clues, however, by watching its posture and expression. Does your pet’s face appear furrowed or “worried”, rather than relaxed and happy? Does it sit hunched or “hunkered” and tense, rather than relaxing and lying down? Lack of mobility can also be a sign of pain.
Another indication of pain is “denning.” An animal in pain will seek a safe place where it won’t be disturbed by other animals. If your pet has forsaken its usual territories or sleeping places for the back of the closet or a spot under the bed, this may be a sign that it is pain or distress and feels vulnerable.
A more obvious indication of pain is a pet’s reaction to touch. If your pet responds to touch by flinching away, hissing, snarling, or even snapping, this is a clear indication of pain. Sometimes this can indicate a localized pain; if the pet doesn’t want to be touched at all, however, it may indicate a broader discomfort.
Incontinence. Many pet owners feel terribly guilty over the natural annoyance they feel when a pet becomes incontinent. They feel they should be more loving, more patient. Incontinence, however, can also be stressful for the pet. As a basic survival mechanism, animals learn not to “mess where they sleep” (for the smell would draw attention to the location of one’s den). When an animal can no longer control when or where it urinates or defecates, you can be sure it is not happy with the situation.
Mental Capacity. Older pets occasionally develop signs of diminished mental capacity. They may seem to “forget” things, such as where a toy is located or what a command means. Such a pet may become confused by its surroundings, and this confusion can develop into fear. (In some cases, this “confusion” may be the result of hearing or vision loss, to which both you and your pet can often adapt.)
Happiness. Determining whether your pet is “enjoying” life is certainly a subjective decision. However, if you have been a keen observer of your pet’s behavior and attitude during its lifetime, you are likely to be able to determine when it no longer seems “happy.” You’ll know when it no longer seems to take any pleasure from its food, its toys, its surroundings—and most of all, from contact with you and the rest of its family. Most pets are tremendously easy to please; when it no longer becomes possibly to raise a purr or a tail-wag, you can be fairly certain that your pet is receiving little joy from life.
Response to Treatment. When a pet becomes ill, our natural response is to provide whatever treatment we can. This may mean tests, medications, even surgery. But drugs have side effects, repeated trips to the vet cause emotional distress, and more invasive treatments take a physical toll. Eventually, we may conclude that our efforts to treat a pet’s illness are more stressful to the pet than the condition itself—and that our efforts to save a pet’s life are actually diminishing, rather than enhancing, the quality of that life.
Making a Decision. Assessing a pet’s quality of life is an ongoing process, not a one-time decision. Initially, we’re likely to attempt to compensate for the problems we see. Pain medication may relieve a pet’s discomfort and improve its mobility. A change in diet may improve a pet’s appetite or provide better nutrition. We may resolve that we’re willing to clean up after a pet and carry it wherever it needs to go, for as long as necessary. But eventually such measures will cease to be effective. The process of assessing “quality of life” is really a question of determining (and deciding) when that point has been reached—and what you intend to do next.
It is often tempting, at this point, to postpone a decision still longer by deciding to “let nature take its course.” Before choosing that course of action (or inaction), however, it’s important to understand that, as a pet owner, you have been thwarting the “course of nature” from the beginning. By ensuring that your pet has food and shelter and is protected from predators, you have already guaranteed that nature will not take its course. By providing medical treatment, you have prolonged the life of your pet far beyond what it could have expected if left to “nature.” In nature, an animal that becomes too ill to obtain food or protect itself will perish quickly, though not necessarily comfortably.
Nor does nature necessarily offer an “easy” death even if you choose to let it “take its course” in the comfort of your home. An animal that cannot breathe easily, cannot eat or digest food properly, cannot control its bodily functions, and can scarcely move or enjoy human contact because of pain, is hardly dying “comfortably.”
This is really what the “quality of life” issue is all about. By usurping nature’s role throughout the life of our pets, we must sometimes also accept its role in determining (and bringing about) the death of a pet. To accept this, we may also have to accept that, in some cases, the quality of life we’re really trying to protect is our own: That we’re allowing our pet to suffer
out of a desire to avoid the anguish we know that we will experience when it dies. And that, ultimately, is the most unselfish act of love we can offer: To end a pet’s suffering, we must choose to accept our own.
Copyright © 2001 by Moira Allen. Reprinted from The Pet Loss Support Page - http://www.pet-loss.net. If you’re grieving the loss of a pet, you’ll find more helpful tips in Moira Allen’s book,
Coping with Sorrow on the Loss of Your Pet, available from Amazon.com at
http://www.amazon.com/exec/obidos/ASIN/1598584537/
|
What Happens after our pet is euthanised? Have you ever wondered what happens in the time between you say your final goodbyes to when you collect the ashes? |
Has grief for a dog who died every overwhelmed you?
Losing a dog always hurts so much, however sometimes the pain is really intense and can be compared to losing a family member. |
Tips for helping your dog deal with the loss of a companion.
Not all dogs will feel the loss of a companion dog, however if the dogs were closely bonded and one of them passes, the surviving dog may have what is often referred to as ‘distress reaction’, which really is just like grief in us humans. |